
Profile: Selecting a profile automatically adjusts all of the settings used in making a print including layer height, print speed, travel speed, etc.Since we’re using PLA, we’ll select ‘Common PLA’ here. Material: This is the material being used for the print.While the Full mode offers more granular control over the print settings, we’re going to use Quickprint for this article so we can cover all the basics. Quickprint allows you to choose a material, profile, platform adhesion aid and also toggle support material on and off. Most sliced gcode files will be between 5MB and 15MB, so anything over 1GB should work fine.īefore we get started, you’ll need to download both your 3D model as well as the slicer software for your 3D printer.Ĭreality Slicer offers two modes for slicing. microSD Card: The Ender 3 Pro includes an 8GB microSD card for transferring files, but some printers include a USB drive.We’ll be using Creality Slicer for this article, but most slicing apps offer similar features and the basic principles are the same. Slicing Software: In order to print your model, you’ll need to convert it from a solid 3D model to a series of slices that can be printed using an app called a slicer.
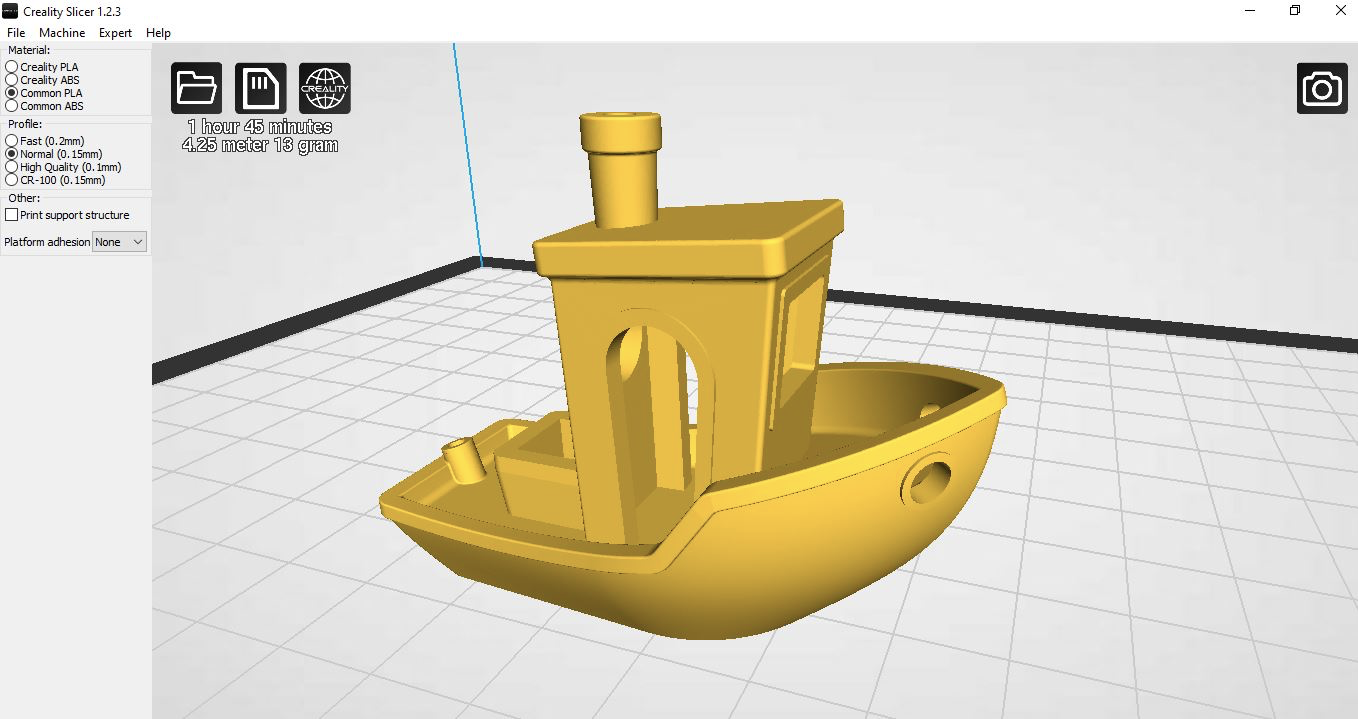
However you can also download STL files from sites such as Thingiverse.


If you need to choose, see our list of best 3D printers. However, other filament-based (aka FDM) printers should work similarly.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
